The unallocated space is simply defined as the area or space on the hard drive of the computer that is available to write data to.
The unallocated space is not viewable to the typical computer user and requires specialized computer forensic software to view and analyze. Unallocated space can contain deleted files or partially deleted files. When a file is deleted, the pointers to the file are removed, but the data remains in unallocated space until such time as the operating system stores another file in the same space, thereby over-writing the data.
Examples :
If the operating system writes a file to a certain space on the hard drive that part of the drive is now “allocated”, as the file is using it the space, and no other files can be written to that section. If that file is deleted then that part of the hard drive is no longer required to be “allocated” it becomes unallocated. This means that new files can now be re-written to that location.
On a standard, working computer, files can only be written to the unallocated space.
If a newly formatted drive is connected to a computer, virtually all of the drive space is unallocated space (a small amount of space will be taken up by files within the file system, e.g $MFT, etc). On a new drive the unallocated space is normally zeros, as files are written to the hard drive the zeros are over written with the file data
-
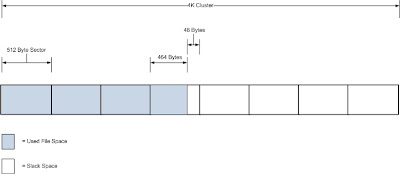
Slack space is a form of internal fragmentation, i.e. wasted space, on a hard disk. When a file is written to disk it’s stored at the “begin...
-
1. first you have to search or scan host that will be targeted 2. Start the the nessus, make sure the service has gone the way of open th...
-
1. Make sure windows xp is installed on Virtual Box 2. Make sure it is connected between the host and guest (BT5 and XP) 3. Cek ip guest t...
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Slack Space
Slack space is a form of internal fragmentation, i.e. wasted space, on a hard disk. When a file is written to disk it’s stored at the “begin...



No comments:
Post a Comment